Security Terms
Security Groups -
A collection of system users used to grant access to Workday. Security Groups are added to security policies to give members permissions to secured items in Workday. Group of users who need to perform actions or access data
Domain Security Policy-
Rules that dictate which security group can view or modify data within the domains
Components of Configurable Security:
- Security Groups
- Domains
- Domain Security Policies
- Business Processes
- Business Process Security Policies
What are the 3 types of security constraints?
- Unconstrained: members have access to available data instances
- Constrained: members will only have access to data for assigned constraints
- Mixed: Members have a mix of constrained and unconstrained
User-based security groups-
These groups are assigned manually to individual users to grant tenant wide access in Workday. Usually intended for administrators that needs system wide access.
Two types of Security Policies-
Domain security policies and Business process security policies.
Domain-
Domains are a collection of items that share the same security, including:
- Tasks
- Reports and report fields
- Web service operations
Domain Security Policies control which security groups have access to data in the domain
- View Security for Securable Item Report
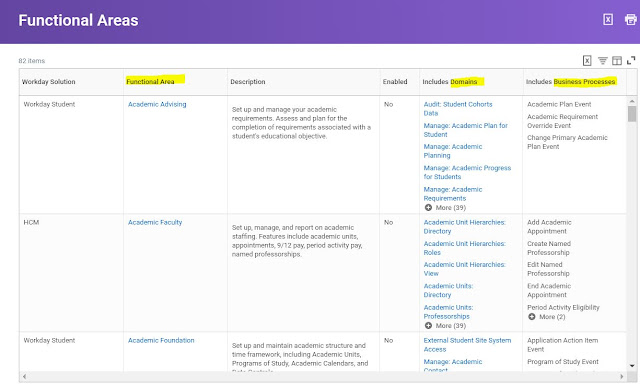
Functional Area-
Represent the main grouping of delivered domains and BP types. These groupings are typically for a specific module or area of Workday, such as Procurement, Integrations, or Personal Data. Functional areas can be enabled or disabled.
Functional Area Report-
Functional Areas report is a "top-down" report which allows you to see a top-down view of Workday functional areas and the domains and business process types in each
Business Process Security Processes-
Business Processes Security Policies control which security groups can participate in the business process (initiate, perform actions, approve, cancel, delegate, etc.)
Have to give permission for multiple policies (ex. Approve, review, etc.)
Each business process type has a single security policy that secures all business process definitions of its type
Steps for Configuring Security:
1. Identify users- who needs access to what?
2. Create security groups- identify existing security group or create a new one for your employees
3. Edit Security Policies- grand view/ modify permissions to domains or grant business process permissions (sometimes domain OR business process or sometimes combo of both)
4.Activate Pending Changes to take effect
5. Test Changes to verify changes made provide the expected access (for both those who got access and those who don't need access)
Workday-Assigned Security Groups
These Security Groups grant GENERAL access and are AUTOMATICALLY assigned by the Workday system
- Assigned to a person
- Based on process such as hiring/ terminating
Ex. Employee as self, worker, all employees, all users, manager's manager
User-Based Security Groups-
These Security Groups grant ADMINISTRATIVE access tenant wide- typically for maintenance/admin groups
- Responsibility applies throughout the system (not just supervisory orgs but for entire tenant)
- User-based security groups are manually assigned to a worker
- Multiple people can be members of the same user-based security group
○ Ex. Benefits admin, compensation admin, payroll admin, report writer, HR admin, etc.
Steps for Creating a User-Based Security Group:
1. Create user-based security group
2. Configure security group on security policies
3. Activate pending security policies
4. Assign users to security group
5. Test (user can create an exit interview, testing it on who should be able vs who should not)
*Don't forget to add group for "administered for security groups" like Security Administrator, otherwise they wont be able to access anything
Role-Based Security Groups:
These Security Groups help identify your support or leadership staff
- Membership is derived based on being assigned an organizational role
- Roles are assigned to organizations (or location hierarchies)
- Roles are assigned to positions, NOT workers
- Roles inherit from superior org if not filled (if configured to do so)
- Access can be defined as constrained and unconstrained
Steps for Creating a Role-Based Security Group:
1. Use "maintain assignable roles" to create or modify assignable roles (supplemental book page 34-35)
2. Create role-based security group
3. Configure security group on security policies
4. Activate security policy changes
5. Assign roles to jobs/ positions to organizations
Test
Job-Based Security Group:
Identify members based on a job criterion
- Job profile
- Job category
- Job family
- Management level
- Work shift
- Include exempt jobs
- Include non-exempt jobs
Automatic membership, Can be constrained or unconstrained
Membership-Based Security Groups:
1. Location (meant for more specific location, not US as a whole)
Grants access to a task based on the location for a worker
Once created, automatically assigned based on users location
Example: for initial deployment of time tracking, only London workers enter time on Workday
2. Organization
Grants access to a task based on the user's membership in org
Once created, automatically assigned based on organization assignments
Example: business unit, company, cost center, pay group, USA as a whole, etc.
Combination Security Groups:
1. Intersection -
Grants access based on membership in ALL of the included security groups
Includes only users who meet all of the specifications
2. Aggregation Security Group -
Includes users who are in ANY of the selected security groups
User does not have to be in every included group
Security Domain
A predefined set of related securable items that include reports, tasks, report fields, data sources, and data source filters
- The securable item that make up a domain cannot be changed
- Each domain has its own security policy that controls access to the security items
Which security group is assigned directly to a worker?
User based security-Tenant wide
Role based security group permissions are given to a worker when their position is linked to what?
Support Role
Editing a security policy takes effect immediately
False- Need to activate
Business Process Policies-
Defines which security groups can participate in the business process
Security group that allows self service access?
Employee as self
Groups of users who need to perform actions or access data?
Security Groups